This phenomenon is very common and negatively affects quality of life; Therefore, you should talk more about the types of diseases, symptoms, causes and treatment methods.
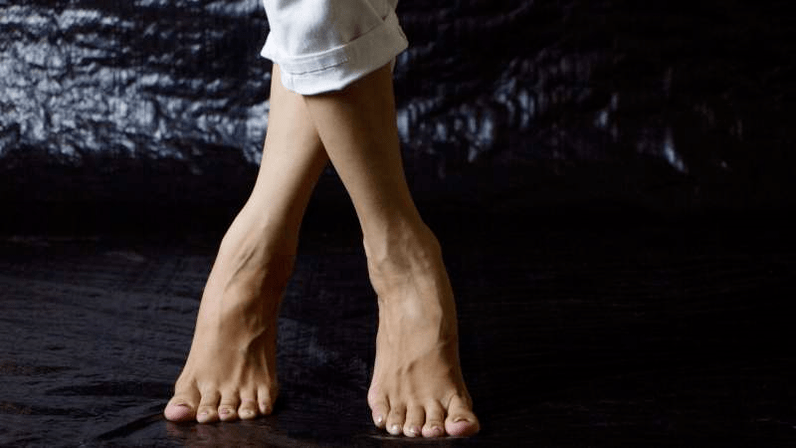

What is Valgus deformation?
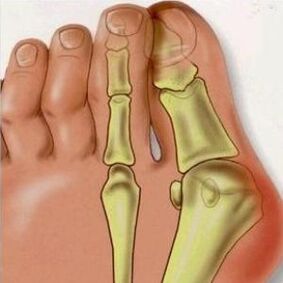
Valgus deformation of the stop is an orthopedic pathology, in which a deformation of the first finger plusnoplance articulation occurs. With it, the first (large) finger in the foot is gradually diverted out, other fingers are deformed. The most characteristic characteristic of the disease is the development of exophytes (bone stretch growth), the foot increases in a transverse size, bending the interior. The diagnosis is made when several indicators change at once: the most characteristic characteristic of the disease is the development of exophytes.
Causes, mechanism
With the deformation of the foot, joint biomechanics is disturbed and the Plusneva bone occurs, which leads to curvature of the foot. The weakness of the leg connection tissues is guilty of deformation of Valgus. With the deformation of the foot, joint biomechanics is disturbed and the Plusneva bone occurs, which leads to curvature of the foot. The thumb can no longer look inside and deviate.
In addition, the patient awaits inflammatory processes where the bone edge is observed, bursitis and changes in bone tissues in the 1st Plus Bone area (his head). All of this leads to the wear of the articulation, arthritis and arthrosis. All of this is complicated for the development of corns and corns.
Reasons:
- Inadequate shoes (high heels and their absence, short or small shoes, narrow fingers);
- Smooth feet;
- Hypermobility of the foot joints;
- Short calf muscle;
- genetics and heredity;
- osteoporosis;
- working conditions (those that are forced to remain for a long time);
- Endocrine system work disorders;
- Overweight.
Types
There are the following varieties of deformation of Valgus of the foot:
- Static deformation is combined with flat feet and occurs as a result of the curvature of the spine. Treatment should start with back treatment.
- The reason for the structural deformation of the foot valgus is an innate abnormality of leg development.
- The cause of the paralytic species is encephalitis or polio.
- Rachitic develops as a result of the lack of vitamin D and other substances. It is also possible as a consequence of a violation of mineral metabolism.
- Traumatic occurs after ligament or fractures ruptures.
- Spastic deformation develops due to muscle cramps.
- With a compensatory, the tendons are reduced and the shape of the ankle joint changes.
- The hyper -control develops after inadequate Clubfoot therapy.
- With the deformation of equine foot planning, the march is disturbed, the sole is very curved inward and, after a long situation, the person feels severe pain. This disease develops as a result of cerebral palsy and is often found in babies.
- When installing a flat valve foot, it does not have a transverse and hollow arrangement.
- The fifth type of deformation develops due to the improper location of the foot directly in the mother in the womb. The front of the foot is very attributed and the heel fuses visually with the leg.
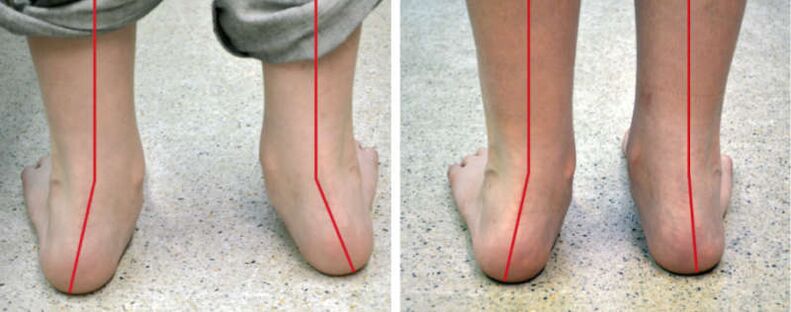
Symptoms at different stages
The disease develops slowly but permanent, therefore, at different stages of the deformation of Valgus from the foot, the symptoms will be different.
In an early stage, there are:
- painful sensations when wearing some types of shoes (with a finger or narrow shoes);
- redness of the skin in the salient area.
In the second stage, there are:
- inflammatory processes in the joints;
- pain;
- swelling;
- Growths become more noticeable.
In the third stage:
- The pain becomes exhaustive and sharp;
- On the foot, there are corns or keratinized skin;
- There is a deformation of all fingers and joints of the foot.
Diagnosis
The main diagnostic methods to determine the deformation of the Valgus of the foot are:
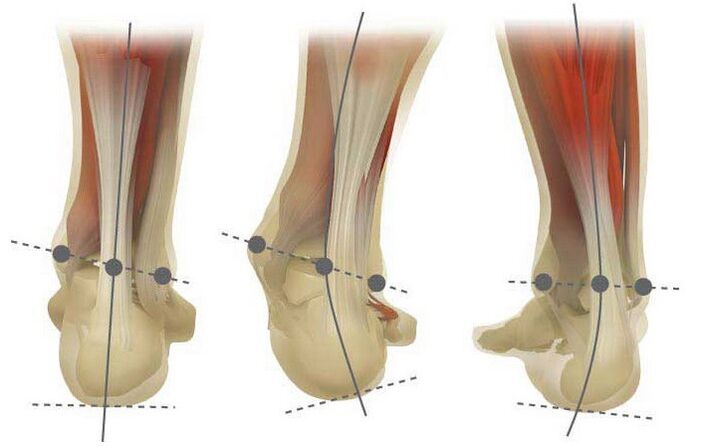
- Clinical inspection. The orthopedist will appreciate the level of fingers and heels deviations, as much as the feet arches are softened and how much it is moved in, in addition to the presence of edema.
- X -Ray. It is performed standing and immediately in 2 projections. Allows you to accurately evaluate all angles between the joints.
- Ultrasound.
- Plantation. This will help determine the size of the load on the foot and at the boring foot stage.
- Computer analysis. Otherwise, a computer study of the foot is called Post -Dometia and allows you to determine the pressure on the feet.
Treatment in children and adults
If the deformation is not too neglected, conservative treatment will be used.
Medical Physical Education
It is better to do so in the hospital, but you can at home. It strengthens the foot and helps to properly distribute the footage in the foot, as well as improving blood circulation and does not allow edema to develop. The complex recommends an orthopedist, or you can handle the video.
Here are the most effective exercises:
The bicycle exercise is effective for the press and the hips, but will help the feet
- Bike. It is effective for the press and the hips, but will help your feet. When you push your leg, pull your foot forward when you pull your foot over yourself.
- Sitting on the floor. We perform based on the floor with our hands. We bend 8 times and extend our legs on our ankle, spread our fingers widely and return them to i. p. Compacting and effectively opening your fingers on your legs 6 times.
- In the chair. We move our feet only with our fingers back and forth. You can hold the 1st and 2nd fingers pencil and draw them on Whatman than you like.
- We stretched our straight legs in a chair in a chair and pull the ankle for ourselves until it stops. We doubled and the 1st finger. After the foot, we extend from ourselves and fold our fingers as much as possible. For the children, rise to socks, walking inside the foot will be effective.
It will be helpful to walk on any nervous surface, sand, (not fast) pebbles and only along a narrow path. A scooter and bicycle will be useful for children because they strengthen the muscles and the joints of the foot. Swimming is also able to strengthen the foot muscles and improve blood circulation.
Orthopedic devices
Several devices are used here, but are selected only with an orthopedist:
- Orthopedic shoes. These shoes must have a tough and high coast and a special leap, longer. It should also have a great disclosure that allows you to use it with other devices (correactors and latches).
- Layers. They can be called for sale by reviewers. Overlays prevent deformations from developing, reducing friction and pressure, and does not allow false joint positions. Made of silicone.
- Tires. Sometimes they avoid surgery, but with advanced stages, they are not recommended. They firmly fix the joints and allow them to be constantly in a calm state, relax the muscles and avoid swelling. All of this allows the joint to take a healthy and correct shape.
- Bandages. They are used for Hallus Valgus, which is similar to tires, but are softer.
- Supinators. So otherwise they call orthopedic insoles. These are mechanical supports that correct the load distribution on the feet and the fixing joints. With valgus deformation, transverse, transverse and frame supervisors can be used.
- Interdiction partitions. They can be called joints, rollers or separators. Facilitate the condition and warn deformation, but they cannot cure dramatically. Normalize the march. They may have locks made of gel or silicone.
- Orthes and tutors. These products are necessary with the deformation of the leg or knee valgus. Their task is a rigid leg fixation. Heralds for sale can also be called insoles, written above.
- Massage rugs. They perform the same functions as irregular surfaces in which it is recommended to walk during the disease. Improve blood flow, avoid swelling, relieve pain.
Physiotherapy
Its task is to alleviate a symptom of pain, prevent stagnant processes in the foot, improve blood circulation and relieve inflammation with swelling:
- Electrophoresis is performed with calcium preparations, chondroitin with glucosamine, anti -inflammatory drugs and painkillers
- Diadinamine therapy. This treatment with electrical currents (frequency 50-100 Hz. ). Pain relieves has a myostimulator effect, improves joint nutrition. In the treatment of the joints, bifurcated electrodes are used. It is against high temperature, hypertension, asthma, epilepsy, radiculitis and neuritis, lesions.
- Electrical stimulation. The effect of pulsed currents with different indicators allows you to train and strengthen the deeper muscles. Because of this, the foot is strengthened. It is performed by applying electrodes to the skin. Duration - No more than 2/3 hours, the course is up to 30 procedures. The against -indications are the same as the therapy with the most damage to the skin.
- Electrophoresis. In this disease, electrophoresis is performed with calcium preparations, chondroitin with glucosamine, anti -inflammatory drugs and painkillers. There is no against -indications, but you need to choose the right medicine.
- Magnetotherapy. It stimulates all cells and accelerates metabolic processes in the joint, used as an auxiliary agent. The electromagnetic field stimulates nerves and muscles.
- Mud applications. Relieve inflammation, swelling and pain. The mud can be sapopelia, hydrothermal and peat, volcanic and sopom. Applied to the feet in the form of "socks" and covered with fabric. Against -Indicated in skin lesions and diabetes.
- Ozokeritis. It heats up and nourishes the joints, interrupts inflammation. Used in the form of baths or "boots".
- Paraffin applications. Parafine is placed on painful legs. Under it, they can apply anti -inflammatory ointment. Relieve inflammation and pain, improve blood supply. Against -indications are the same as the treatment of mud and ozkerita.
- Night baths. Relax the muscles of the foot, relieve pain and inflammatory processes. The most applicable for salt and dirt baths.
- Acupuncture. This will help eliminate some causes of feet deformation development if caused by any nervous or endocrine system disease: you only need to act correctly at the right points.
Operational correction
With very neglected deformation of the feet and a vegetation covered exophy, the operation is the only effective method. About one hundred types of operations are used to treat deformation today.
The most effective is:
Recovery begins on the 2nd day, when the operated is allowed to move the fingers
- surgical removal of growth (except it can grow again);
- balancing of periarticular muscles;
- Deformed bone reconstruction operation;
- Joint Fixation - Attodesis;
- Operation to restore ligaments and their correct location;
- Implementation of the joint or tendon;
- Operation in positive bone head excision - exostctomy;
- The operation to change the angle between bones and removal of the phalanx or more is osteotomy. It may be chevarin, proximal or distal;
- Dozens of other operations.
Recovery begins on day 2, when the operated is allowed to move the fingers. After 1, 5 weeks, you can start walking, but you cannot step on a co -optimal area.
It is possible to charge the leg in 4-5 weeks. After 6 months, you can use jumps and start playing sports.
During rehabilitation, it is recommended to suffer therapy with shock waves, which improves blood circulation in tissues and reduces edema. The physiotherapy methods described above will be useful.
Folklore methods of treatment
It is not the best method of correction of the deformation of valgus of the feet and gets rid of the bone. But you can try.
The compresses are popular.
They use iodine, cabbage sheet, fish (river), aspirin, waiting, snow, castor oil:
- The cabbage leaf can be applied to the affected joint, wrapped in a handkerchief and go to the bed.
- The hope rubs for the first time on the skin, after heating the leg and going to the bed.
- Baths with iodine. One teaspoon of iodine per liter of water is required. Sound your legs 1/3 hours and move well.
But practice shows that the folk treatment of the curvature of Valgus of the feet is ineffective and can harm.

Prevention
Complaints in this disease happen because the weakness of ligaments and muscles is not so simple.
Prevention includes:
- Wearing the right shoes: natural, no narrow sock and in a small jump;
- Treatment of boring feet in time;
- Rest on the legs;
- load regulation;
- relaxing baths;
- Insoles or orthopedic supervisors.
What should be shoes?
It is best to order orthopedic shoes in special stores and after consulting an orthopedist.
The shoes should be:
- soft;
- The sock must be wide;
- Kabluk is required - up to 4 cm. ;
- The backdrop and supervisor should be dense and high (the height of the background - 3 cm of heel).